In our modern world, the quality of the air we breathe indoors has become a critical concern. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), indoor air can be two to five times more polluted than outdoor air. This alarming statistic underscores the importance of air filtration systems in maintaining a healthy living and working environment. In this guide, we will unpack the science behind air filtration, explore the different types of filters available, discuss the benefits of using high-quality air purifiers like the AirDoctor line, and incorporate insights from several key studies.
The Science of Air Filtration
Air filtration is the process of removing particles and contaminants from the air. These contaminants can include dust, pollen, pet dander, mold spores, bacteria, viruses, smoke, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Effective air filtration involves the use of filters that can trap these particles, preventing them from circulating in the air we breathe.
Types of Airborne Particles
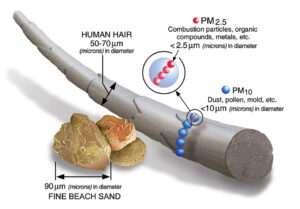
Particulate Matter (PM): These are tiny particles suspended in the air, which include dust, pollen, and mold spores. They can be classified into PM10 (particles with a diameter of 10 microns or less) and PM2.5 (particles with a diameter of 2.5 microns or less). PM2.5 particles are particularly dangerous as they can penetrate deep into the lungs and even enter the bloodstream.
Biological Contaminants: These include bacteria, viruses, and mold spores. They can cause infections and allergic reactions. According to a meta-analysis conducted by the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, dampness and mold in homes are associated with a 30% to 80% increase in respiratory and asthma-related health issues. The study reviewed by the Institute of Medicine (IOM) highlights the significant impact of mold on respiratory health.
Chemical Pollutants: VOCs, such as formaldehyde and benzene, are emitted from building materials, furniture, and household products. These chemicals can cause various health issues, including respiratory problems and cancer.
Gaseous Pollutants: These include carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide, which are often produced by combustion processes.
Understanding Indoor Air Quality and Biological Pollutants
When we think of air pollution, we often envision smog-filled skies and industrial emissions. However, air pollution can be a significant issue right inside our homes. Indoor air quality is influenced by various factors, including biological pollutants that can affect our health more than we might realize.
What Are Biological Pollutants?
Biological pollutants are living organisms that can significantly impact indoor air quality. They include a range of contaminants such as animal dander, dust mites, cockroach parts, infectious agents like bacteria and viruses, and pollen. These pollutants can be present in every home, regardless of how clean they appear. Key conditions that support their growth include moisture and nutrients, which can be found in numerous household locations like bathrooms, basements, carpets, and furniture.
The Scope of the Problem
Studies have shown that up to 50% of all buildings have conditions conducive to the growth of biological pollutants, particularly in damp environments. For instance, surveys conducted in homes across the northern U.S. and Canada reveal a high prevalence of damp conditions, which promote the growth and accumulation of these pollutants. This issue is exacerbated in warm, moist climates where humidity levels are higher.
Health Effects of Biological Pollutants
Exposure to biological pollutants can lead to various health issues, primarily allergic reactions, infections, and toxic responses. Allergies are the most common, with symptoms ranging from mild discomfort, such as watery eyes and sneezing, to severe asthma attacks. According to a meta-analysis conducted by the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, building dampness and mold are associated with a 30% to 80% increase in respiratory and asthma-related health issues. This highlights the critical need to manage indoor air quality effectively.
Types of Air Filters
Air filters are essential components of air purification systems. The two main types of filters used in air purifiers are HEPA filters and carbon filters.
HEPA Filters
HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters are designed to capture 99.97% of particles as small as 0.3 microns. They work through a combination of three mechanisms: inertial impaction, interception, and diffusion.
- Inertial Impaction: Larger particles, such as dust and pollen, collide with the fibers in the filter and get trapped.
- Interception: Medium-sized particles follow the airflow stream and are intercepted by the fibers.
- Diffusion: The smallest particles move erratically due to Brownian motion and eventually collide with the fibers.
Advanced HEPA Filters
Advanced HEPA filters, like the UltraHEPA filters used by AirDoctor, can capture particles as small as 0.003 microns, providing an even higher level of air purification. These filters are particularly effective against viruses, bacteria, and smoke particles.
Carbon Filters
Carbon filters, also known as activated carbon filters, are highly effective at removing gaseous pollutants and odors. The activated carbon has a large surface area and porous structure, allowing it to adsorb gases and volatile organic compounds. This makes carbon filters essential for eliminating harmful chemicals and unpleasant smells from indoor air.
Insights from “Single-Stage Air Filtration of Particles and Gaseous Contaminants in Buildings: A Literature Study”
A comprehensive study published in the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, highlights the importance of air filtration technologies in improving indoor air quality. The study reviews various air filtration technologies and their effectiveness in removing both particulate matter and gaseous contaminants. Here are some key takeaways from the study:
Filtration Efficiency
- Mechanical Filters: These filters, including HEPA filters, are highly efficient at removing particles. They can capture up to 99.97% of particles with a diameter of 0.3 microns or larger. However, they are not effective at removing gaseous pollutants.
- Electrostatic Filters: These filters use an electrostatic charge to capture particles. They have lower filtration efficiency compared to mechanical filters and can produce by-products like ozone.
- Adsorbent Filters: These filters, which use materials like activated carbon, are effective at removing gaseous pollutants. However, they are not efficient at particle removal.
- Photocatalytic Oxidation (PCO): This technology uses a catalyst, typically titanium dioxide, to degrade VOCs. It is effective at gas removal but not suitable for particle removal and can produce harmful by-products.
- Electrospun Nanofiber Filters: These emerging technologies show promise for the simultaneous removal of particles and VOCs. They offer high particle removal efficiency and can degrade VOCs using additives like activated carbon or titanium dioxide.
Pressure Drop
The energy consumption of a ventilation system is affected by the pressure drop across the filter. Mechanical filters tend to have a higher pressure drop due to clogging over time, which reduces their efficiency. Electrostatic filters and electrospun nanofiber filters generally have a lower pressure drop, making them more energy-efficient.
By-Products
Certain air filtration technologies can produce by-products that degrade indoor air quality. For instance, electrostatic filters can generate ozone, and PCO filters can produce partial oxidation by-products that are harmful. Adsorbent filters can re-emit pollutants when saturated.
Insights from “Allowing Buildings to Breathe”
The study “Allowing Buildings to Breathe” discusses the innovative concept of breathing walls, which provide high-quality indoor environments using less energy while combating urban air pollution. Here are some highlights from their findings:
Breathing Walls and Dynamic Insulation
Breathing walls are designed to allow ventilation air to flow through the building envelope, filtering airborne pollutants and recovering conduction heat loss simultaneously. These walls use dynamically insulated panels that act as both an air filter and a heat exchanger. The study highlights several benefits of this technology:
- Energy Efficiency: By using the building envelope as a source of ventilation, the need for extensive ducting and mechanical systems is reduced, leading to significant energy savings.
- Improved Air Quality: The dynamic insulation material in breathing walls acts as an efficient filter, removing particulate matter and gaseous pollutants from the air.
- Sustainability: Breathing walls offer a sustainable solution to urban air pollution and energy consumption, aligning with the goals of sustainable development.
Filtration Efficiency of Dynamic Insulation
The study by Imbabi and Peacock provides a detailed analysis of the filtration efficiency of dynamic insulation. They found that fibre-based insulation materials, such as Glasswool, can achieve high filtration efficiency for a wide range of particle sizes. The filtration efficiency improves over time as particles accumulate in the insulation material, enhancing its effectiveness.
The Health Benefits of Air Filtration
Effective air filtration can have profound benefits for your health and well-being. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Reduced Respiratory Problems
Airborne particles, such as dust, pollen, and mold spores, can trigger respiratory issues like asthma and allergies. By removing these particles from the air, air purifiers can help reduce the frequency and severity of these problems.
2. Improved Cardiovascular Health
Exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) has been linked to cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. High-quality air purifiers can reduce the concentration of these harmful particles, thereby lowering the risk of cardiovascular problems.
3. Enhanced Immune System
Air purifiers can help eliminate bacteria and viruses from the air, reducing the likelihood of infections. This is particularly important in places where people are in close contact, such as offices and schools.
4. Better Sleep Quality
Clean air can improve sleep quality by reducing irritants that can cause nighttime coughing and sneezing. This is especially beneficial for individuals with allergies or asthma.
5. Protection Against Harmful Chemicals
Carbon filters can remove VOCs and other harmful chemicals from the air, which are linked to a variety of health issues, including cancer. By reducing exposure to these chemicals, air purifiers can contribute to long-term health benefits.
The AirDoctor Advantage
When it comes to air purification, AirDoctor stands out for its advanced filtration technology and comprehensive approach to indoor air quality. Let’s take a closer look at what makes AirDoctor air purifiers exceptional.
UltraHEPA Filter
AirDoctor air purifiers are equipped with UltraHEPA filters, which can capture 99.99% of particles as small as 0.003 microns. This is significantly more effective than standard HEPA filters, providing unparalleled protection against the smallest and most harmful airborne contaminants.
Carbon VOC Filter
In addition to the UltraHEPA filter, AirDoctor air purifiers also use a carbon VOC filter. This filter is specifically designed to target and adsorb volatile organic compounds and odors, ensuring that the air is not only clean but also free of harmful chemicals and unpleasant smells.
Multi-Stage Filtration System
AirDoctor’s 3-stage filtration system includes:
- Pre-Filter: Captures larger particles, extending the life of the other filters.
- Carbon VOC Filter: Adsorbs gases, odors, and VOCs.
- UltraHEPA Filter: Traps the smallest particles, including bacteria, viruses, and smoke.
Features of AirDoctor Air Purifiers
AirDoctor offers a range of air purifiers to suit different room sizes and needs. Here are some key features of their models:
AirDoctor 1000:
- Room Size Coverage: 285 sq. ft. 4x/hour, 570 sq. ft. 2x/hour
- CADR (smoke): 152
- Filters: 1 Pre-Filter, 1 Carbon/VOC Filter, 1 UltraHEPA Filter
- Recommended Filter Change Frequency: Every 6 months for Carbon/VOC Filter and UltraHEPA Filter
- Sound Levels: 34 dB (lowest speed), 54 dB (highest speed)
- Dimensions: 9” (W) x 9” (D) x 23” (H)
- Weight: 10 lbs
AirDoctor 2000/2000i:
- Room Size Coverage: 305 sq. ft. 4x/hour, 610 sq. ft. 2x/hour
- CADR (smoke): 162
- Filters: 1 Pre-Filter, 1 Carbon/VOC Filter, 1 UltraHEPA Filter
- Recommended Filter Change Frequency: Every 6 months for Carbon/VOC Filter, Every 12 months for UltraHEPA Filter
- Sound Levels: 40 dB (lowest speed), 55 dB (highest speed)
- Dimensions: 13.85″ (W) x 6.6″ (D) x 18.72″ (H)
- Weight: 10 lbs
AirDoctor 2500:
- Room Size Coverage: 305 sq. ft. 4x/hour, 610 sq. ft. 2x/hour
- CADR (smoke): 220
- Filters: 1 Pre-Filter, 1 Carbon/VOC Filter, 1 UltraHEPA Filter
- Recommended Filter Change Frequency: Every 6 months for Carbon/VOC Filter, Every 12 months for UltraHEPA Filter
- Sound Levels: 40 dB (lowest speed), 55 dB (highest speed)
- Dimensions: 13.85″ (W) x 6.6″ (D) x 18.72″ (H)
- Weight: 10 lbs
AirDoctor 3500/3500i:
- Room Size Coverage: 630 sq. ft. 4x/hour, 1,260 sq. ft. 2x/hour
- CADR (smoke): 340
- Filters: 1 Pre-Filter, 1 Carbon/VOC Filter, 1 UltraHEPA Filter
- Recommended Filter Change Frequency: Every 6 months for Carbon/VOC Filter, Every 12 months for UltraHEPA Filter
- Sound Levels: 39 dB (lowest speed), 59 dB (highest speed)
- Dimensions: 15.75″ (W) x 8.75″ (D) x 23″ (H)
- Weight: 18 lbs
AirDoctor 5500/5500i:
- Room Size Coverage: 1,043 sq. ft. 4x/hour, 2,086 sq. ft. 2x/hour
- CADR (smoke): 556
- Filters: 2 Permanent Pre-Filters, 2 Carbon/VOC Filters, 2 UltraHEPA Filters
- Recommended Filter Change Frequency: Every 6 months for Carbon/VOC Filter, Every 12 months for UltraHEPA Filter
- Sound Levels: 30 dB (lowest speed), 50 dB (highest speed)
- Dimensions: 16” (D) x 16” (D) x 28.75” (H)
- Weight: 33 lbs
Image Source: AirDoctor
Portability and Ease of Use
AirDoctor air purifiers are designed with user convenience in mind. Features such as built-in recessed handles and hidden casters make them easy to move from room to room. The sleek and modern design ensures they fit seamlessly into any home or office décor.
The AirDoctor Commitment to Quality
AirDoctor is committed to providing high-quality air purification solutions that are both effective and accessible. Their products are backed by scientific research and are independently tested to ensure they meet the highest standards of performance. By choosing AirDoctor, you are investing in a product that prioritizes your health and well-being.
Cleaning Up
In conclusion, the importance of air filtration in maintaining a healthy indoor environment cannot be overstated. With the rise in pollution and the increasing prevalence of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, having a reliable air purifier is essential. AirDoctor air purifiers, with their advanced UltraHEPA and carbon VOC filters, offer superior protection against a wide range of airborne contaminants. By investing in an AirDoctor air purifier, you can breathe easy knowing that you are creating a healthier and more comfortable living and working environment for yourself and your loved ones.