The modern world is full of hidden stressors that drain energy, disrupt hormones, and accelerate aging. One of the most overlooked players in this equation? Mitochondria—the tiny power plants within every cell that determine how well we produce energy, regulate hormones, and recover from stress. For decades, mainstream health advice has focused on treating symptoms rather than addressing the root causes of hormonal imbalances, low energy, and metabolic dysfunction. However, emerging research points to mitochondrial health as the foundation for hormonal regulation—including testosterone, estrogen, and overall endocrine balance. If your mitochondria are compromised, everything from metabolism to mood takes a hit. Let’s explore how mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to hormonal decline, the impact of modern lifestyle choices, and how you can restore mitochondrial function to enhance vitality, strength, and longevity.
The Importance of Testosterone
Testosterone is often thought of as the male hormone, but it plays a critical role in both men and women. It is essential for muscle growth, fat metabolism, bone density, mood regulation, and overall energy levels. While men naturally produce more testosterone than women, both genders require it for optimal health. Maintaining proper testosterone levels is not just about physical performance—it’s a cornerstone of long-term health and quality of life.
Why Testosterone is Crucial for Health
Muscle Growth & Strength: Testosterone drives protein synthesis and muscle development, helping to maintain lean muscle mass and prevent sarcopenia (muscle loss with age).
Fat Metabolism & Weight Control: Higher testosterone levels contribute to a lower body fat percentage and improved metabolic efficiency.
Bone Density & Joint Health: It supports bone mineralization and reduces the risk of osteoporosis, making it essential for long-term skeletal strength.
Mood & Mental Well-Being: Optimal testosterone levels are linked to reduced anxiety, improved motivation, confidence, and a greater sense of well-being.
Cognitive Function & Brain Health: Research shows that testosterone plays a role in maintaining cognitive sharpness, memory retention, and mental clarity as individuals age.
Libido & Reproductive Health: Testosterone is a primary driver of libido and overall sexual function in both men and women, impacting fertility and hormonal balance.
Energy Levels & Endurance: It directly influences mitochondrial energy production, ensuring sustained stamina and faster recovery from physical exertion and stress.
Cardiovascular Health: Testosterone has been associated with better heart function, improved circulation, and balanced cholesterol levels.
Signs of Low Testosterone
When testosterone levels decline, it can lead to a cascade of health problems, including:
Chronic fatigue and low energy
Increased body fat, especially around the midsection
Loss of muscle mass and reduced physical performance
Mood swings, irritability, and depression
Brain fog, difficulty concentrating, and memory loss
Low libido and sexual dysfunction
Weakened bones and increased risk of fractures
Given the wide-reaching effects of testosterone, ensuring its optimal levels through lifestyle modifications is crucial for overall health, performance, and longevity.
The Mitochondrial Connection to Hormones
Mitochondria are known for their role in ATP (energy) production, but their influence extends far beyond metabolism. They are the gatekeepers of hormone synthesis. Within the mitochondria, cholesterol is converted into pregnenolone—the precursor to all steroid hormones, including testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, and cortisol. When mitochondrial function is impaired, hormone production declines, leading to fatigue, metabolic issues, mood disorders, and even cognitive decline. Given the stressors of modern living—processed foods, environmental toxins, blue light exposure, and chronic stress—it’s no wonder that mitochondrial dysfunction is rampant. The good news? You can repair and optimize mitochondrial function through simple yet powerful lifestyle interventions.
How the Modern World is Destroying Testosterone
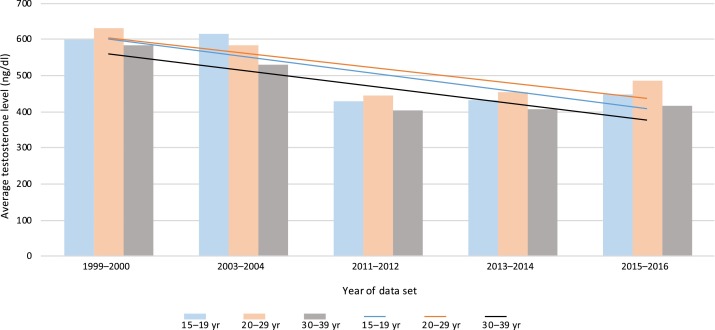
Testosterone levels have been plummeting over the last few decades, and the modern environment is a major culprit. Several key factors contribute to this decline:
Endocrine Disruptors: Chemicals found in plastics, personal care products, and household items mimic estrogen and interfere with testosterone production.
Chronic Stress and Cortisol Overload: Stress raises cortisol, a hormone that directly inhibits testosterone production and increases fat storage.
Sedentary Lifestyles: Lack of movement leads to reduced testosterone production, slower metabolism, and muscle loss.
Poor Sleep Hygiene: Inadequate sleep reduces testosterone levels, disrupts circadian rhythm, and weakens mitochondrial function.
Nutrient Deficiencies: A diet lacking key nutrients such as zinc, magnesium, and vitamin D negatively impacts testosterone production.
Electromagnetic Field (EMF) Exposure: Constant exposure to wireless radiation and blue light can damage mitochondrial function and disrupt hormone production.
Insulin Resistance: A Silent Hormone Disruptor
Insulin resistance is one of the most pervasive yet overlooked factors contributing to hormonal imbalance and mitochondrial dysfunction. When cells become resistant to insulin, the pancreas compensates by producing more of it, leading to chronically elevated insulin levels. Over time, this metabolic dysfunction results in systemic inflammation, oxidative stress, and a breakdown in cellular communication, all of which directly impact hormone production and overall health.
How Insulin Resistance Disrupts Hormones
Increased Fat Storage: Excess insulin promotes fat storage, particularly visceral fat, which is metabolically active and releases inflammatory cytokines that further impair mitochondrial function.
Elevated Cortisol Levels: Insulin resistance is often accompanied by increased cortisol, the stress hormone, which suppresses testosterone production and promotes fat accumulation.
Testosterone Conversion to Estrogen: Higher levels of visceral fat activate the enzyme aromatase, which converts testosterone into estrogen. This leads to an imbalance in sex hormones, contributing to symptoms such as fatigue, low libido, and mood swings.
Disrupted Mitochondrial Function: Mitochondria process glucose for energy, but when insulin resistance prevents proper glucose uptake, cells become energy-starved, leading to chronic fatigue and metabolic dysfunction.
Inflammation & Oxidative Stress: Chronically high insulin levels trigger widespread inflammation and oxidative stress, which accelerate mitochondrial degradation and impair the body’s ability to produce essential hormones.
Signs of Insulin Resistance
Many people are unaware that they have insulin resistance until it has progressed to prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. Some key signs include:
Unexplained weight gain, especially around the midsection
Frequent hunger and sugar cravings
Energy crashes after meals
Brain fog and difficulty concentrating
Skin tags, dark patches of skin (acanthosis nigricans)
High triglyceride and low HDL cholesterol levels
Hormonal imbalances, including low testosterone and irregular menstrual cycles
One of the biggest culprits behind mitochondrial dysfunction is insulin resistance—a condition where the body’s cells stop responding properly to insulin. This leads to elevated blood sugar levels, increased fat storage, and systemic inflammation, all of which negatively impact mitochondrial efficiency and hormone production. In both men and women, insulin resistance contributes to low testosterone and estrogen imbalances. The excess body fat from insulin resistance also increases aromatase activity, an enzyme that converts testosterone into estrogen, further exacerbating hormonal dysregulation. The takeaway? Improving insulin sensitivity is crucial for restoring mitochondrial function and hormonal balance.
Strategies to Revitalize Mitochondrial Function (and Hormonal Health)
1. Cold Therapy: Activate Mitochondrial Renewal
Cold exposure triggers mitophagy—the process of clearing out damaged mitochondria and stimulating the production of new ones. Research suggests that regular cold exposure can improve insulin sensitivity, increase resilience to stress, and support hormonal regulation. Whether through ice baths, cold showers, or cryotherapy, incorporating cold therapy into your routine can significantly enhance mitochondrial function.
2. EMF Protection: Safeguard Cellular Energy
Electromagnetic fields (EMFs) from Wi-Fi, cell phones, and electronics create oxidative stress, which damages mitochondria and impairs hormone production. Research suggests that chronic EMF exposure can disrupt mitochondrial function, contributing to fatigue, hormonal imbalances, and cognitive decline. Protecting yourself from excessive EMF exposure is a crucial step in maintaining mitochondrial and endocrine health. Aires Tech offers EMF protection technology designed to neutralize these effects, supporting overall cellular function.
3. Optimize Light Exposure: Natural Sunlight and Red Light Therapy
Light exposure significantly impacts mitochondrial function and hormone production. Morning sunlight regulates the circadian rhythm, while excessive blue light at night disrupts melatonin—a crucial mitochondrial antioxidant. Red light therapy has been shown to enhance ATP production and support endocrine function. To maximize mitochondrial health:
Get morning sunlight daily.
Avoid blue light exposure at night (use blue-light blocking glasses).
Sleep in a pitch-black room to optimize melatonin production.
Use red light therapy to stimulate mitochondrial activity.
4. Intermittent Fasting & Ketosis: Give Mitochondria a Break
Mitochondria require periods of rest to function optimally. Constant eating leads to metabolic stress, while fasting allows mitochondria to repair and regenerate. Studies show that intermittent fasting and ketogenic diets promote autophagy (cellular cleanup), reduce oxidative stress, and support hormone balance. Implementing a fasting window or a low-carb, high-fat diet can improve mitochondrial efficiency and overall well-being.
5. Strength Training: Build Resilient Mitochondria
Exercise is one of the most effective ways to enhance mitochondrial efficiency. Strength training, in particular, increases mitochondrial biogenesis and boosts testosterone production. Compound movements like squats and deadlifts stimulate growth hormone and anabolic pathways, improving overall metabolic health. Prioritize:
Heavy resistance training (4-6 rep range for compound lifts)
Full-body workouts incorporating lower-body exercises
Proper recovery strategies to allow mitochondria to repair
6. Ditch Processed Foods: Prioritize Real, Nutrient-Dense Eating
The modern diet is packed with ultra-processed foods that fuel inflammation, disrupt metabolism, and impair mitochondrial efficiency. Seed oils (soybean, canola, corn), refined sugars, and artificial additives all contribute to insulin resistance and hormonal dysregulation.
To support mitochondrial function and hormonal balance, adopt the JERF (Just Eat Real Food) method by prioritizing:
Nutrient-dense animal proteins like grass-fed beef, pasture-raised eggs, and wild-caught fish
Healthy fats such as grass-fed butter, tallow, coconut oil, and extra virgin olive oil
Organic fruits and vegetables for fiber, polyphenols, and essential micronutrients
Fermented foods like sauerkraut, kimchi, and kefir for gut health and hormone regulation
Supplementing with mitochondrial-supporting antioxidants can further combat oxidative stress:
Chlorella & Spirulina: Aid detoxification, boost cellular energy, and improve vitality.
Astaxanthin: Enhances mitochondrial function, reduces inflammation, and protects against oxidative damage.
Nutrient-dense animal proteins like grass-fed beef, pasture-raised eggs, and wild-caught fish
Healthy fats such as grass-fed butter, tallow, coconut oil, and extra virgin olive oil
Whole, organic fruits and vegetables for their fiber, polyphenols, and essential micronutrients
Fermented foods like sauerkraut, kimchi, and kefir to support gut health, which is closely linked to hormone regulation
Chlorella & Spirulina: These nutrient-dense algae help detoxify heavy metals, support cellular energy production, and enhance overall vitality.
Astaxanthin: A powerful antioxidant known to improve mitochondrial function, reduce inflammation, and protect against oxidative stress.
7. Methylene Blue: A Game-Changer for Mitochondrial Function
Methylene blue is an underrated yet powerful compound that supports mitochondrial respiration and energy production. Originally used as a medical dye, methylene blue acts as an electron donor in the mitochondrial electron transport chain, effectively enhancing ATP production. Studies suggest that it can improve cognitive function, reduce oxidative stress, and even support neuroprotection. To incorporate methylene blue safely:
Use pharmaceutical-grade methylene blue from a reputable source.
Start with a low dose and monitor the effects.
Consult a healthcare professional for guidance on usage.
The Bottom Line: Mitochondrial Health is the Foundation of Well-Being
Modern lifestyles take a toll on mitochondrial function, leading to widespread hormonal imbalances, metabolic disorders, and chronic fatigue. But by making strategic lifestyle shifts—embracing cold exposure, intermittent fasting, proper light exposure, avoiding toxic oils, strength training, and incorporating methylene blue—you can reclaim your energy, resilience, and hormonal balance. Mitochondria are more than just energy producers; they are the gatekeepers of long-term health and vitality. Prioritize their function, and your body will reward you with optimal hormone levels, improved metabolic function, and a renewed sense of well-being.